
The progress in artificial intelligence has made it possible to remotely identify legal entities.
The Official Gazette today released a Communiqué from the Ministry of Treasury and Finance that revises the General Communiqué of the Financial Crimes Investigation Board, and this amendment is now active.
Initially, remote identification methods were used exclusively for setting up ongoing business relationships with individuals. However, with technological advancements in the financial sector, there’s now a necessity to establish remote customer relations not just with individuals but also with legal entities registered in the trade registry.
CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENT
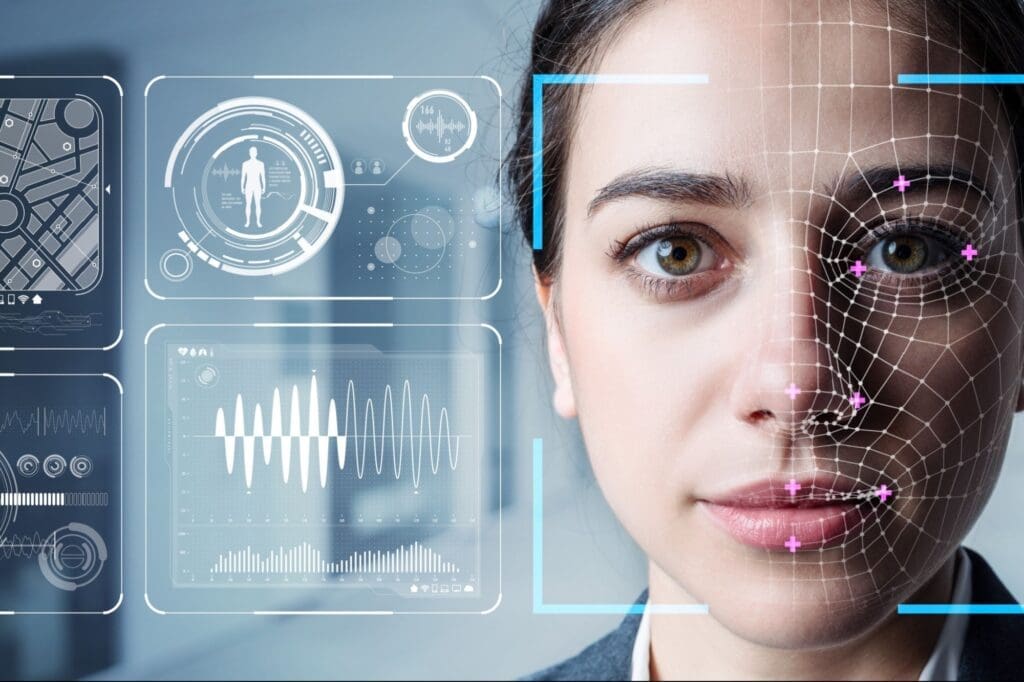


The recently published Communiqué details the procedures and principles related to the remote identification methods for legal entities registered in the trade registry, allowing the use of artificial intelligence in this process.
Due to the technological aspects of remote identification, the Communiqué requires certain protections. In particular, when employing services from third parties, there is a need for certification in information security management. Furthermore, when artificial intelligence is used for remote identification, there is a requirement to provide reports on certain technical issues.
WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE?

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field dedicated to creating computer systems capable of mimicking human cognitive functions. Its ultimate goal is to equip machines with human-like intelligence, enabling them to perform complex tasks. This broad discipline includes a range of subfields:
- Machine Learning (ML): ML allows computers to improve their performance over time by processing data. They autonomously learn from tasks through algorithms, enhancing their capabilities through model building and data analysis.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This area enables computers to understand, produce, and interact with human language, with uses from text analysis to chatbot interactions.
- Image Processing: Focused on visual data, this field enables computers to recognize and analyze images and videos, identifying objects, faces, and various visual elements.
- Robotics: This subfield enhances the cognitive and physical abilities of robots, finding applications in automation, autonomous vehicles, and manufacturing robots.
- Expert Systems: These specialized AI systems possess in-depth knowledge in particular areas such as medicine, law, or finance, offering advice at an expert level.
- Deep Learning: Originating from artificial neural networks, deep learning uses large datasets to create complex models, forming the basis for many current AI applications.
AI has significantly impacted numerous industries, transforming aspects of everyday life. It powers personal digital assistants, content recommendation systems, autonomous driving, medical diagnostics, financial analysis, and countless other applications.
You may also like this content
- AI in Education: Transforming Learning Experiences Today
- iOS 18 is Out: AI Features and Compatible iPhones Explained
- How Web3 and AI Integration Creates New Value Opportunities
Follow us on TWITTER (X) and be instantly informed about the latest developments…







