Solar Panel Production with 3D Printers Begins in Orbit

Dcubed aims to manufacture solar panels directly in space in 2027. Thanks to the ARAQYS system, the company aims to reduce costs and eliminate payload issues.
As commercial space flights continue to accelerate, the demand for solar panels for spacecraft is increasing rapidly. To meet this need, Dcubed is developing the ARAQYS system, which will be capable of manufacturing solar panels directly in orbit.
The Goal of In-Orbit Panel Production
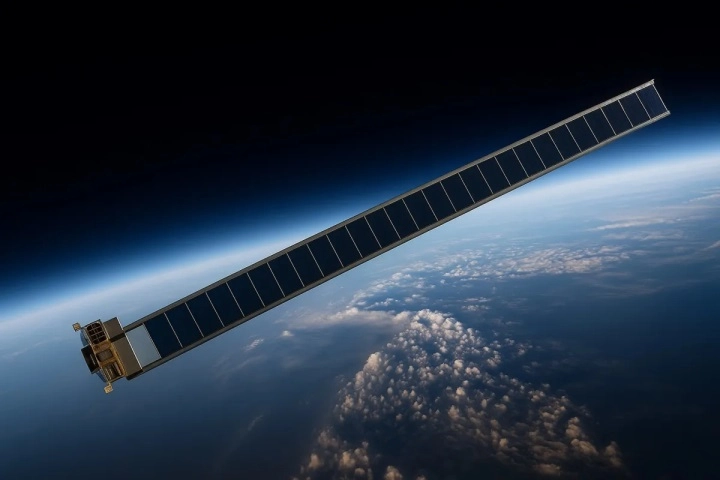

The energy needs of satellites in orbit are generally met by solar panels. Space is an extremely suitable energy source as it lacks the obstructing effects of the atmosphere, weather conditions, and the day-night cycle. However, the weight and transportability issues of existing panels require additional mechanisms during launch.
These mechanisms, which allow the panels to unfold, create extra mass and must withstand the acceleration, vibration, and acoustic stresses of the rocket takeoff. This situation increases costs while reducing the available payload capacity.
Dcubed aims to overcome these problems with ARAQYS. The system manufactures the panels directly in orbit, eliminating the folding and unfolding mechanism. Consequently, the cost per kilowatt is predicted to drop significantly.
ARAQYS is built upon an ultra-thin, flexible, and lightweight solar blanket. Once the satellite reaches orbit, the blanket unfolds, and subsequently, a 3D printer prints the rigid back structure of the panels. The powerful UV rays of space rapidly harden the resin, creating a durable structure. This method allows for a manifold reduction in costs.
Dcubed is planning a series of trial missions to validate the system. The first mission aims to construct a 60 cm long panel this year. This will be followed by a 1-meter version and an operational demo with a 2 kW capacity in 2027. Following success, commercial products are expected to be offered for sale.