Quantum Computers: Unlocking the Future of Computing
Quantum computers are no longer a distant dream of science fiction—they are real, and they are reshaping the way we think about computation. Unlike classical computers, which rely on bits that are either 0 or 1, quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously thanks to a phenomenon called superposition. This capability allows quantum computers to process enormous amounts of information in parallel, solving problems that would take classical machines millennia to tackle.
Another key feature is entanglement, where qubits become linked so that the state of one instantly affects the state of another, no matter the distance between them. Einstein famously called this “spooky action at a distance,” but today it is a proven and experimentally verified property of quantum systems. Entanglement enables quantum computers to perform calculations with a level of coordination and speed that classical computers simply cannot match.

The potential applications of quantum computing are staggering. In cryptography, quantum computers could break widely used encryption methods, threatening the security of everything from private messages to bank transactions. RSA encryption, elliptic curve cryptography, and other protocols that secure the digital world could become obsolete once sufficiently powerful quantum computers are developed.
But quantum computing is not just about breaking things—it’s about creating solutions that were previously impossible. Quantum simulations could revolutionize medicine by modeling molecular interactions with extreme precision, allowing scientists to design new drugs and materials at an atomic level. Energy storage and renewable technologies could be optimized through quantum calculations, creating batteries and energy systems far more efficient than today’s standards. Complex logistical problems, like city traffic optimization and global supply chains, could also be solved with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Despite the promise, quantum computers remain in their infancy. Current machines are small, noisy, and fragile, capable of only a limited number of qubits. Error correction and stability are major challenges, and fully scalable, fault-tolerant quantum computers are still years—if not decades—away. However, the race is on. Governments, research institutions, and tech giants are investing heavily in quantum research and post-quantum cryptography, preparing for a future where quantum machines play a central role in technology and security.
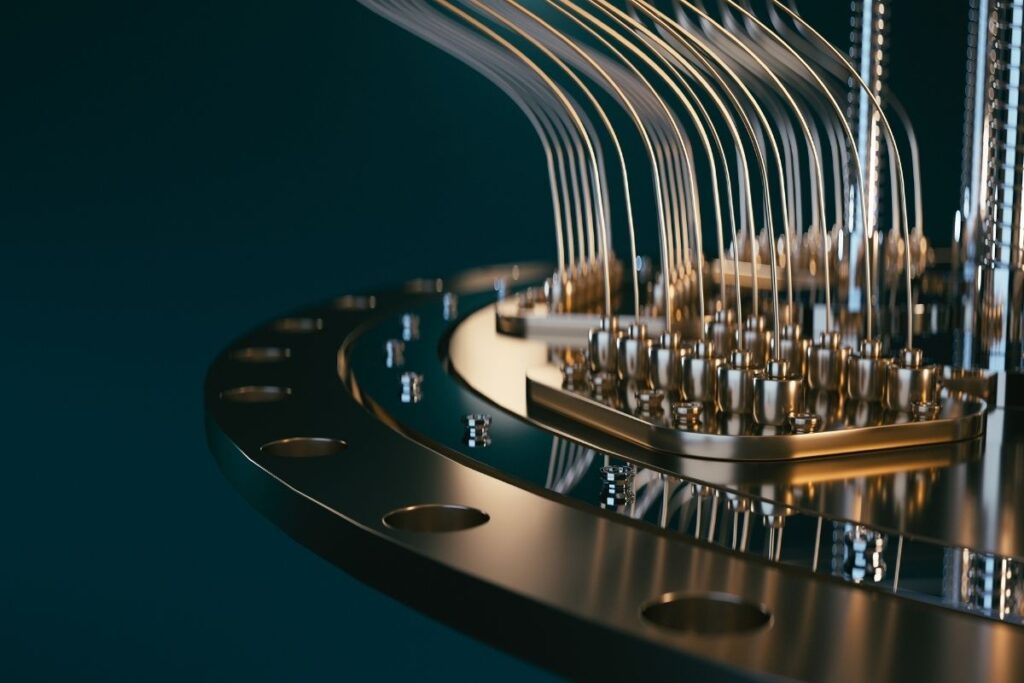
The excitement around quantum computing lies in its dual nature: it can be both a threat and a tool for unprecedented progress. It forces us to rethink the limits of computation, security, and scientific discovery. While the average user may not feel the impact today, the quantum revolution is quietly shaping the technologies that will define our future.
In the end, quantum computers represent the ultimate fusion of science, mathematics, and engineering, unlocking doors that humanity could only dream of a few decades ago. They are not just machines—they are a glimpse into the fundamental workings of the universe itself, offering both wonder and responsibility in equal measure.