Renewable Energy Set to Surpass Coal by 2026

According to the IEA, renewable sources are expected to overtake coal as the leader in global electricity generation by 2025 or 2026. During the same period, nuclear power production is also preparing to break records.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) announced that global electricity demand is projected to increase by an average of more than 3% annually until 2026. This growth is primarily driven by expanding industrial, transport, and data center usage, especially in emerging economies in Asia. A significant portion of this demand will be met by renewable energy, natural gas, and nuclear sources.
According to the IEA’s mid-year update report, electricity consumption will increase by 3.3% in 2025 and 3.7% in 2026. This rate significantly surpasses the 2.6% average observed between 2015 and 2023. Although the growth rate slightly decreases compared to the 4.4% increase in 2024, one of the strongest trends of the last decade continues.
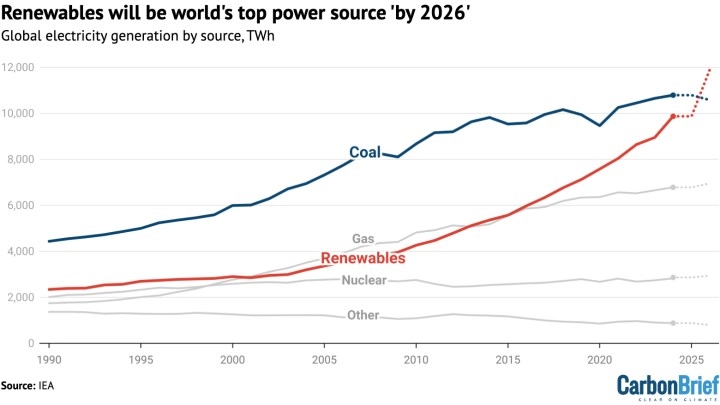
Renewables Overtaking Coal

The report predicts that renewable sources will become the world’s largest electricity generation source by 2025 or 2026, surpassing coal for the first time. During the same period, nuclear energy production is also expected to reach record levels. The restarting of power plants in Japan, strong production performance in the US and France, and new projects in Asia will contribute to this increase. Furthermore, natural gas plants are increasingly substituting the use of coal and oil.
With this transition, carbon emissions from electricity generation are expected to plateau in 2025 and show a slight decrease in 2026. 60% of the global demand increase will come from emerging economies in Asia. China’s electricity consumption is projected to rise by 5.7% and India’s by 6.6% in 2026. In the US, the growth of data centers will ensure that demand remains above 2% annually until 2026. In the European Union, electricity demand is expected to increase by approximately 1% in 2025, with further acceleration anticipated in 2026.
Prices Increased, Competition Imbalanced
In the first half of 2025, wholesale electricity prices in the European Union and the US increased by 30% to 40% compared to the previous year. This is primarily due to tightening natural gas markets. Although prices remain below the 2023 average, they are still significantly higher than in 2019. Additionally, the increasing occurrence of negative wholesale prices highlights an urgent need for investments in grid flexibility, energy storage, and flexible consumption. Industrial competition varies significantly across regions. In Europe, electricity prices for energy-intensive sectors are twice as high as in the US and considerably higher than in China.
This report paints a clear picture of the shifting landscape in global energy. What are your thoughts on the implications of renewable energy becoming the primary source of electricity worldwide?











